Karibaev Talgat Bolatovich
+7 (7172) 64-78-74
diz_nrcv@mail.ru
Saryarkinsky district, street 150 years of Abay 22/3
ACTIVITIES OF THE LABORATORY
The activities of the Laboratory for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases (hereinafter – DID) include:
Conducting reference laboratory studies of biomaterial delivered from veterinary facilities in various regions of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Carrying out monitoring laboratory studies of biomaterial from animals and birds of wild fauna.
Conducting an analysis of the epizootic situation for infectious diseases at veterinary agricultural facilities, as well as wild fauna.
Implementation of visits of specialists for the selection of biomaterial at the sites of veterinary facilities.
Implementation of advisory assistance to veterinary specialists at the regional and district levels.
The object of research is farm animals and birds, various species of wild animals and birds of wild fauna, bacteria of various nomenclature, antigens, vaccines, feed, soil, water and other objects of veterinary supervision.
Research methods – when conducting research, epizootological, serological, bacteriological, molecular biological research methods are used.
DEPARTMENT OF BACTERIOLOGY
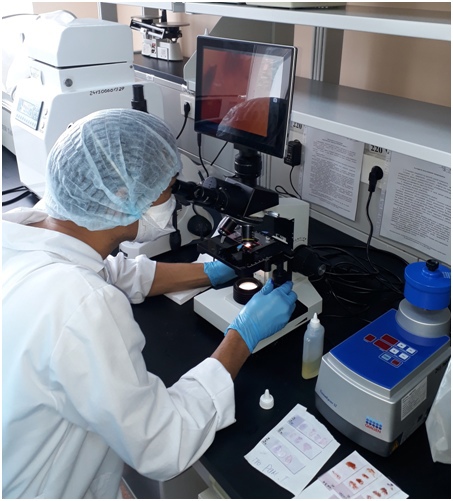
Bacteriological studies in the DIZ laboratory are used to isolate bacteria and study their properties to make a microbiological diagnosis.
General information about the department and staffing
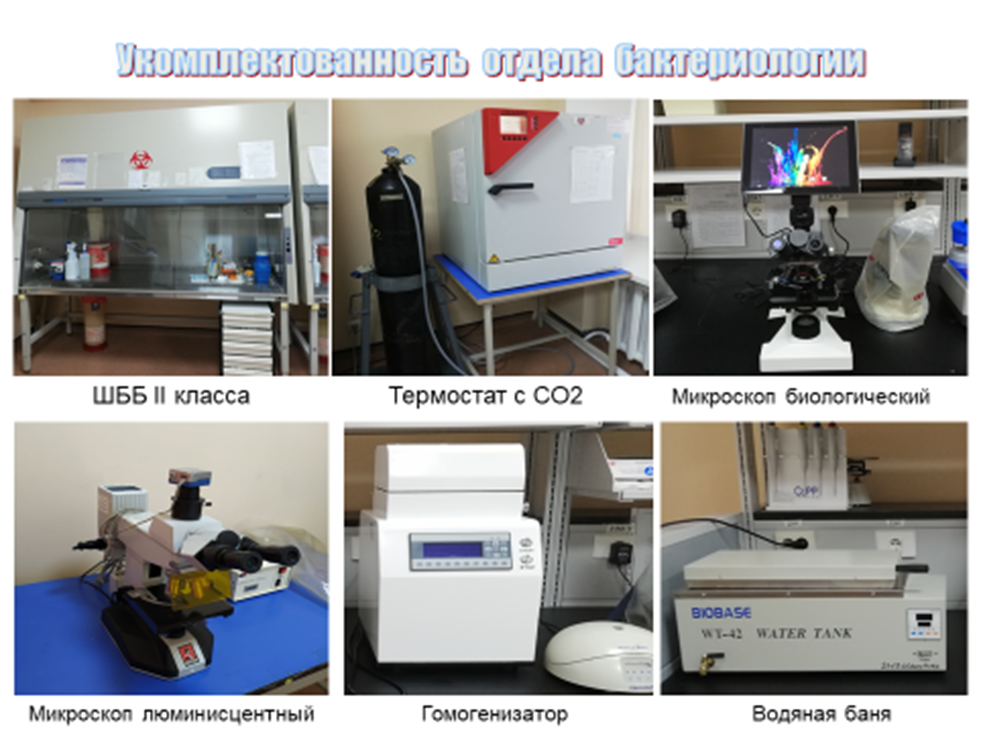
Rooms for bacteriological research in the laboratories of the DIZ in Nur-Sultan are equipped with biosafety cabinets of the 2nd level and all the necessary equipment for bacteriological research (thermostats, biological microscopes, water baths, anaerostats, etc.).
The laboratory also uses laboratory animals as biological models for conducting biological samples with infection in certain diseases to identify pathogens and determine their virulent properties.
Bacteriological studies are carried out for diseases such as brucellosis, tuberculosis, paratuberculosis, anthrax, listeriosis, staphylococcus aureus, campylobacteriosis, pasteurellosis, anaerobic infections (emkar, bradzot, anaerobic enterotoxemia), enterobacterial infections (salmonellosis, colibacteriosis).
SEROLOGY DEPARTMENT
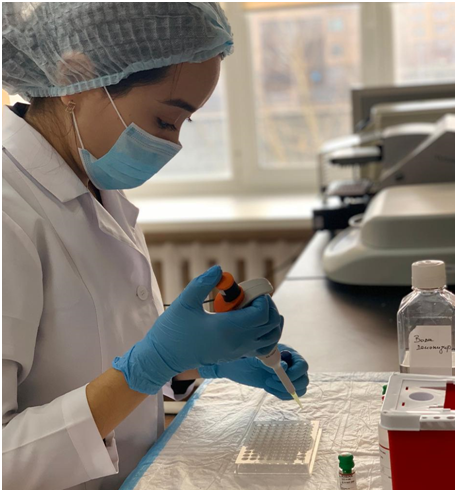
Serological reactions in the DIZ laboratory are used for diagnostic purposes, identifying the source of infection, serotype, immune background and determining the epizootic situation by conducting screening studies among animals and birds in agriculture, as well as wild fauna. The principle of serological reactions is based on the interaction of antibodies and antigens in the animal body.
General information about the department and staffing
Applied methods:
– Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect antibodies or antigen to such diseases as brucellosis, foot and mouth disease, Newcastle disease, leukemia, chlamydia, rhinopneumonia of horses, infectious rhinotracheitis, infectious anemia of horses, avian influenza, viral diarrhea, African and classical swine fever, bluetongue, paratuberculosis, Schmallenberg’s disease, etc.;
For brucellosis, in addition to ELISA, the complement fixation reaction (RCC), the rosbengal test (RBP) and the immune diffusion reaction with O-polysaccharide antigen (RID with OPS antigen) are used;
For leukemia, in addition to ELISA, an immune diffusion reaction (RID) is used, as well as a hematological analysis according to the leukocyte formula;
For rabies, the methods of immunochromatographic analysis (ICA) and the direct method of immunoluminescent microscopy (PMIM) using diagnostic anti-rabies fluorescent immunoglobulin (IDAF) are used;
DIZ laboratories in Nur-Sultan and Almaty are equipped with all the necessary equipment and instruments for serological testing, such as an ELISA analyzer in the kit, automatic and semi-automatic dispensers, water baths, etc.

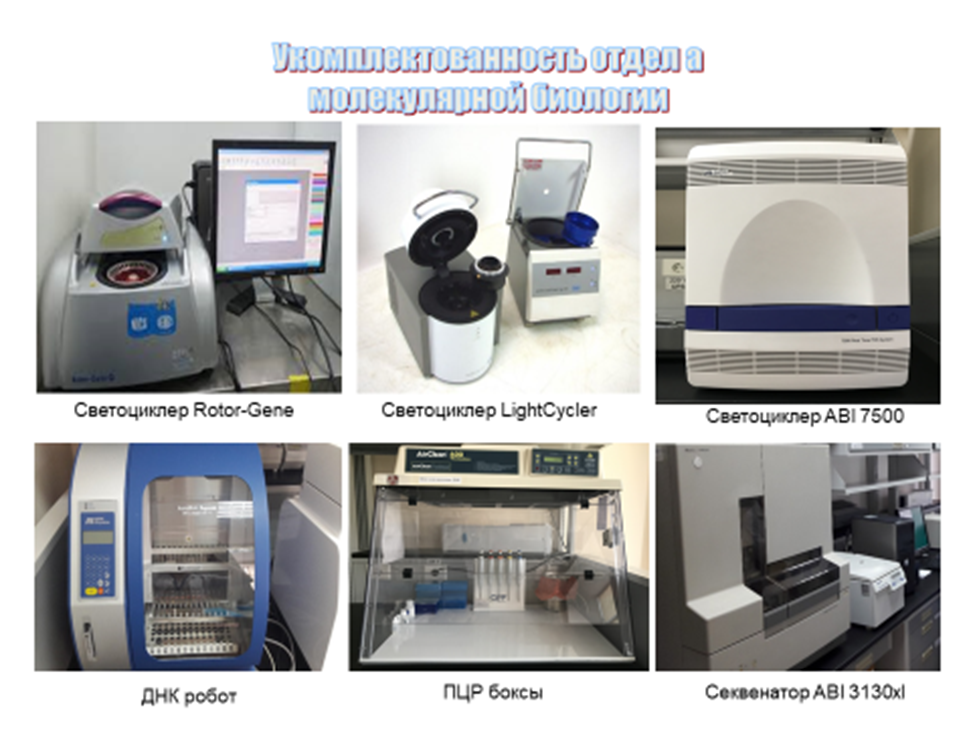
DEPARTMENT OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
The DIZ laboratory uses the method of molecular genetic studies of biological material, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), taking into account the results both in real time (real-time PCR) and taking into account in electrophoresis, in order to identify nucleic acids (DNA/ RNA) of certain microorganisms, to diagnose infectious diseases and determine the epizootic situation among animals and birds in agriculture, as well as wild fauna.
PCR is used to repeatedly increase DNA fragments specific to certain microorganisms.
The method of sequencing the nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA gene of bacterial cultures is also used.
General information about the department and staffing
For conducting molecular biological research in the laboratories of the DIZ of the city of Nur-Sultan and Almaty, standard zones for dividing rooms are used:
1-DNA/RNA extraction room equipped with a level 2 biosafety cabinet and all necessary equipment for isolation (high-speed centrifuges for microtubes, thermostats for test tubes, thermal stirrers, etc.).
2-room for preparing master mixes equipped with a PCR box and all necessary equipment.
3rd room for PCR. Equipped with PCR machines for real-time PCR and classical PCR.
4th Room. room for electrophoresis.
The PCR method in the DIZ laboratory is used to isolate DNA / RNA of such pathogens as brucellosis, foot and mouth disease, b. Newcastle, leukemia, chlamydia, RTI, HPAI, bovine viral diarrhea, ASF, CSF, bluetongue, tuberculosis. paratuberculosis b. Schmallenberg, listeriosis, leptospirosis, etc.
DEPARTMENT OF EPIZOOTOLOGICAL MONITORING
Ensuring monitoring of pathogens of especially dangerous infections of farm animals and birds is one of the main ways in creating the foundations of a biological safety system in the Republic of Kazakhstan.
At present, the study of the epizootic situation of especially dangerous human and animal infections has become an urgent problem for many countries of the world, including our state.
The main activities of the epizootic monitoring department are:
generation of reports for epizootological analysis based on the results of the study and forecasting of expected diseases for subsequent years;
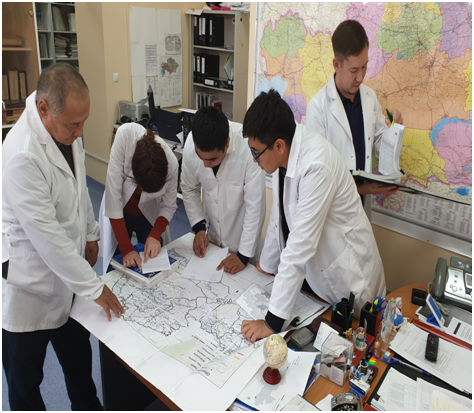
use of a geographic information system based on the ArcGis Desktop platform to create geographic maps with an epizootic situation;
carrying out visits to veterinary facilities for sampling from farm animals;
organization of activities for the implementation of expeditions for sampling among wild fauna;
monitoring of information sources of foreign countries on outbreaks of animal diseases;
accounting of information on animal diseases in the world received from official sources such as the International Epizootic Bureau (OIE), the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Rosselkhoznadzor, PubMed CDC, etc.
The most dangerous diseases periodically manifest themselves in certain countries, the pathogens of which are capable of being transmitted from a sick animal to a healthy one, and often to humans – such as foot-and-mouth disease, anthrax, brucellosis, rabies, etc. This determines the possibility of continuous transmission of pathogens of an infectious disease, the mass nature of the defeat animals and a tendency to a wide territorial distribution.
Department Information
To perform functional duties, the department is staffed with a staff of 5 units in the city of Nur-Sultan and 2 units in the branch of the city of Almaty, as well as the following equipment:
personal computers and laptops on the Windows platform;
ArcGis Desktop, version 10.6;
means of radio communication;
geolocation devices;
mobile laboratory based on the Kamaz vehicle;